
Defining health information exchange: scoping review of published definitions
[ad_1] 1. 1st PC (178) Web page: 1st Providers Choice, Solution Provider Unknown US Health Information Exchange (HIE) refers to the process of reliable and interoperable electronic health-related information sharing conducted in a manner that protects the confidentiality, privacy, and security of the information. 2. 4Med (188) Web page: Educational Resource for Healthcare Information Technology Unknown US Health Information Exchange

Electronic health record’s effects on the outpatient office visit and clinical education
[ad_1] INTRODUCTION The use of an electronic health record (EHR) by a provider during an office visit has been equated to ‘texting while driving’ and thus raises concerns that a provider’s observation, communication, problem solving and development of trusting relationships could be impacted.1 We agree that a person should not be texting while driving, yet what is wrong with texting

Ethnicity recording in primary care computerised medical record systems: an ontological approach
[ad_1] RESULTS Data was available for 2,059,453 patients across 110 practices in England and Wales, utilising the Read 2 classification. Mean valid ethnicity recording was 48.97% (n =1,008,667) across the sample population. Of those identified with a valid ethnicity recording, 96.14% (n = 969,740) were recorded to have a definite code. 3.71% (n = 37,443) and 0.15% (n = 1,487)
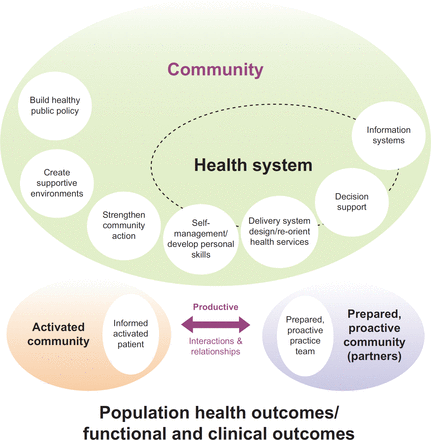
An ‘integrated health neighbourhood’ framework to optimise the use of EHR data
[ad_1] Introduction Persisting systems gaps and fragmentation of care within and between health care teams in primary and secondary care are the key issues being addressed by most national health systems, examples being the Australian primary health care (PHC) strategic framework,1 NSW State Health Plan2 and eHealth blueprint.3 The long-suffering patient has to deal with fragmented roles and responsibilities compounded

Visualization approaches to support healthy aging: A systematic review
[ad_1] Abstract Background Informatics tools have the potential to support the growing number of older adults who are aging in place. Many tools include visualizations (data visualizations and visualizations of physical representations). However, the role of visualizations in supporting aging in place remains largely unexplored. Objective To synthesize and identify gaps in the literature evaluating visualizations (data visualizations and visualizations

The UK National Data Guardian for health and care’s review of data security, consent and opt-outs: leadership in balancing public health with rights to privacy?
[ad_1] THE UK MODEL OF PRIVACY PROTECTION AND ROLE OF THE NATIONAL DATA GUARDIAN The Data Protection Act 19986 implemented the 1995 European Data Protection Directive. It provides the legal framework for the UK’s data protection procedures. The Data Protection Act 1998 provided an exemption from the general prohibition of processing sensitive data for reasons of substantial public interests, which

Tightrope walking towards maximising secondary uses of digitised health data: A qualitative study
[ad_1] We approached 28 potential interviewees (declined, n = 1; no response or subsequently could not be contacted, n = 4), leading to 23 interviews with participants throughout the UK and in Australia (n = 1), Canada (n = 2) and the USA (n = 1). One interviewee (Scottish Government) subsequently withdrew consent, reporting new workplace regulations against giving interviews,

In this issue – Don’t make assumptions about integrated systems, data quality, utilisation of technology or access to routine data
[ad_1] INTEGRATED SYSTEMS Two of the articles in this issue describe conceptually and practically how we can work in a more integrated way. The first looks at an integrated health neighbourhood and the second at electronic prescribing and medicine administration system. This issue opens with an article about how conceptually we need to move towards an integrated health neighbourhood.1 Much

Implementation of data management and effect on chronic disease coding in a primary care organisation: A parallel cohort observational study
[ad_1] DISCUSSION Data management activities were implemented in the primary care organisation we studied. This implementation was associated with significantly greater increases in coding for chronic conditions studied compared to other Canadian practices. There is limited evidence on which interventions are most effective in improving data quality.56,57 Repeated assessments, feedback and training may be effective.57 However, this represents a significant

Establishing data-intensive learning health systems: an interdisciplinary exploration of the planned introduction of hospital electronic prescribing and medicines administration systems in Scotland
[ad_1] The identification of different stakeholder experiences and needs is important to catalyse the development of an integrated data strategy to support the effective use and reuse of HEPMA data. Adding to the existing international implementation-related literature, we have identified a number of micro-, meso- and macro-factors that are important in facilitating this in the Scottish context. In particular, our

In this issue: Realising benefits and that informatics is all about the patient
[ad_1] Introduction This issue has papers that can be broadly grouped into two themes: (1) Realising benefits and (2) the central importance of providing public and patients usable systems. We are publishing several articles which relate to the theme of Realising benefits from health informatics. Our leading article reviews the open source paradigm1 – a key element of that discussion

The critical components of an electronic care plan tool for primary care: an exploratory qualitative study
[ad_1] Methods Our qualitative study consisted of three focus groups followed by nine semi-structured interviews. These were conducted at the Jen Center for Primary Care, an academic internal medicine practice at Brigham and Women’s Hospital that provides care to 19,000 patients. One-third of its diverse population derives from the hospital’s underserved urban surroundings, a similar fraction receives public insurance and

A lack of a comparator group makes it hard to be sure whether computerised medical record system implementation achieved a better or worse outcome
[ad_1] The difficulty of drawing conclusions without a control population Burke et al.1 draw conclusions about the impact of using a computerised medical record (CMR) system. However, we recommend exercising caution about the 5-year finding as there was no comparator group. There is therefore no means of establishing what would have happened to glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) in patients in this

The adoption of an electronic health record did not improve A1c values in Type 2 diabetes
[ad_1] Results The overall mean (CI) A1c values for the before-EHR, after-EHR and five-years were 7.07 (6.91 – 7.23), 7.33 (7.14 – 7.52) and 7.19 (7.06 – 7.32), respectively, labelled All in Figure 1. There was a small but significant increase in A1c values between before-EHR and after-EHR, p = .04, but there were no significant differences between before-EHR and

How do clinical information systems affect the cognitive demands of general practitioners? Usability study with a focus on cognitive workload
[ad_1] Results Sixty-seven respondents completed the online survey. A precise estimate of the responses rate was not possible because we did not know the number of GPs who received the invitation. However, a gross estimate could be between 0.5 and 1%, based on a possible number of GPs receiving the survey of 5,000–10,000. The distribution of systems used by participants

National health models and the adoption of eHealth and ePrescribing in primary care – new evidence from Europe
[ad_1] Definitions and methods ePrescribing has been defined as a prescriber’s ability to electronically send an accurate, error-free and understandable prescription directly to a pharmacy from the point of care.29 This definition was used in this study and explicitly includes the electronic transfer of prescription (ETP) as an integral part of the ePrescribing process. A literature review was carried out

In this issue: Time to replace doctors’ judgement with computers
[ad_1] Abstract Informaticians continue to rise to the challenge, set by the English Health Minister, of trying to replace doctors’ judgement with computers. This issue describes successes and where there are barriers. However, whilst there is progress this tends to be incremental and there are grand challenges to be overcome before computers can replace clinician. These grand challenges include: (1)

Primary care physicians’ perspectives on computer-based health risk assessment tools for chronic diseases: a mixed methods study
[ad_1] Abstract Background Health risk assessment tools compute an individual’s risk of developing a disease. Routine use of such tools by primary care physicians (PCPs) is potentially useful in chronic disease prevention. We sought physicians’ awareness and perceptions of the usefulness, usability and feasibility of performing assessments with computer-based risk assessment tools in primary care settings. Methods Focus groups and
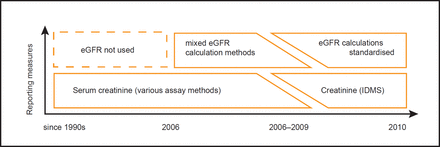
Improving the measurement of longitudinal change in renal function: automated detection of changes in laboratory creatinine assay
[ad_1] Abstract Introduction Renal function is reported using the estimates of glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). However, eGFR values are recorded without reference to the particular serum creatinine (SCr) assays used to derive them, and newer assays were introduced at different time points across the laboratories in the United Kingdom. These changes may cause systematic bias in eGFR reported in routinely
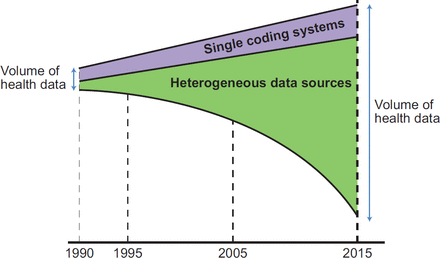
Using ontologies to improve semantic interoperability in health data
[ad_1] Abstract The present–day health data ecosystem comprises a wide array of complex heterogeneous data sources. A wide range of clinical, health care, social and other clinically relevant information are stored in these data sources. These data exist either as structured data or as free-text. These data are generally individual personbased records, but social care data are generally case based

Health care provider perceptions of a query-based health information exchange: barriers and benefits
[ad_1] Results A total of 5618 surveys were mailed, and 615 were returned (11%). The majority of surveys were completed by physicians (N = 315, 51%), followed by APRNs (N = 122, 20%) and PAs (N = 97, 16%) (Table 1). The most common specialties were family medicine (N = 149, 24%) and internal medicine (N = 94, 15%). The
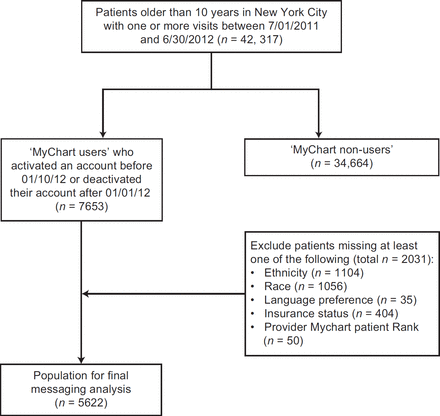
Characteristics of electronic patientprovider messaging system utilisation in an urban health care organisation
[ad_1] METHODS This study was conducted at a Federally Qualified Health Center (FQHC) in New York City. The FQHC uses an EpicCare EHR system (Epic Systems, Verona, WI) with an associated patient portal called MyChart that allows patients to exchange electronic messages with their health care providers. A retrospective cross-sectional study was performed using data recorded in the FQHC’s EHR
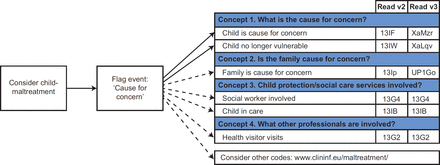
A simple clinical coding strategy to improve recording of child maltreatment concerns: an audit study
[ad_1] Child safeguarding (Box 1) includes the recording of concerns and information about vulnerable children in the child’s medical record.1 There is substantial under-recording of child maltreatment and maltreatment-related concerns in primary care records,2,3 which places children at increased risk of harm.4–6 Recording of concerns underpins sharing of information between practitioners, failure of which is highlighted repeatedly as an important

Using information to deliver safer care: a mixed-methods study exploring general practitioners’ information needs in North West London primary care
[ad_1] The analysis revealed a number of factors constraining the use of information in general practice. First, the communication gap between primary and secondary care needs to be addressed. Sometimes GPs are unaware of their patients’ recent tests, scans and medication changes as their hospital colleagues often omit to include these findings in reports to practices. In addition, when these

Journal of Innovation in Health Informatics: building on the 20-year history of a BCS Health peer review journal
[ad_1] Abstract After 20-years as Informatics in Primary Care the journal is renamed Journal of Innovation in Health Informatics. The title was carefully selected to reflect that: informatics provides the opportunity to innovate rather than simply automates; implementing informatics solutions often results in unintended consequences, and many implementations fail and benefits and innovations may go unrecognised; health informatics is a
