
A proposal for developing a platform that evaluates algorithmic equity and accuracy
[ad_1] Solutions to improve algorithm transparency and performance and promote health equity Starting from the premise that any complex societal problem must first be measured before it can be solved, Mayo Clinic and Duke School of Medicine entered a collaboration with Optum/Change Healthcare focused on analysis of their data consisting of >35.1 billion healthcare events and over 15.7 billion insurance

EDQM OCCL study reports low compliance of “kids’ cosmetics”
[ad_1] A study by the European Network of Official Cosmetics Control Laboratories (OCCLs) indicates that “kids’ cosmetics” continue to fail to comply with European quality and safety regulations, finding that 25% of samples were non-compliant with legislative requirements. Decorative cosmetics, including temporary hair colour products (54% of the samples), nail varnishes (39%), body and face paints (25%), eye products (22%),

Call for better systems and data to support artificial intelligence for pandemic response
[ad_1] The COVID-19 pandemic has been a major disruption for the world, and countries have struggled to manage the spread of the virus and its many consequences with variable success. To control a novel infectious agent with unknown behaviour and effects, it is essential to be able to access and analyse large quantities of data in near real time. Some

Driving digital health transformation in hospitals: a formative qualitative evaluation of the English Global Digital Exemplar programme
[ad_1] There is currently a strong international drive towards creating digitally-enabled health systems and settings, with governments embarking on large-scale health information technology (HIT) change initiatives to improve quality, safety and efficiency of health and care.1 2 For example, in the USA, the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) initiative launched in 2009 combined over US$25.9 billion

Exploring stakeholder attitudes towards AI in clinical practice
[ad_1] Results A total of 27 articles were included3–29 of which most (16, 59%) targeted clinicians,3–18 8 (30%) focused on consumers (including patients),19–26 1 (4%) on health executives27 and 2 (7%) on industry stakeholders comprising AI vendors, researchers and regulators.28 29 Detailed study descriptions are provided in the online supplemental appendix and summary results are listed in table 1. Most
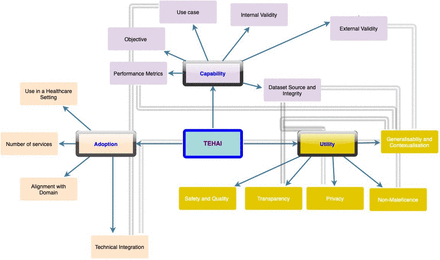
Evaluation framework to guide implementation of AI systems into healthcare settings
[ad_1] Abstract Objectives To date, many artificial intelligence (AI) systems have been developed in healthcare, but adoption has been limited. This may be due to inappropriate or incomplete evaluation and a lack of internationally recognised AI standards on evaluation. To have confidence in the generalisability of AI systems in healthcare and to enable their integration into workflows, there is a
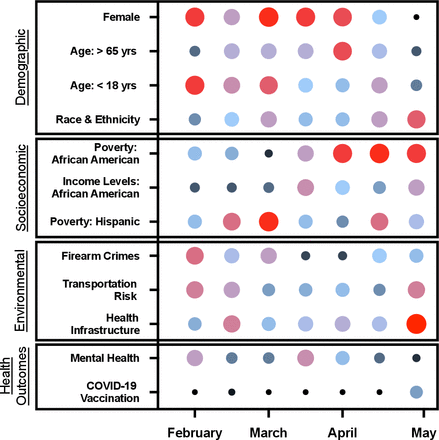
Influence of social determinants of health and county vaccination rates on machine learning models to predict COVID-19 case growth in Tennessee
[ad_1] Abstract Introduction The SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) pandemic has exposed health disparities throughout the USA, particularly among racial and ethnic minorities. As a result, there is a need for data-driven approaches to pinpoint the unique constellation of clinical and social determinants of health (SDOH) risk factors that give rise to poor patient outcomes following infection in US communities. Methods We combined

Review of study reporting guidelines for clinical studies using artificial intelligence in healthcare
[ad_1] Abstract High-quality research is essential in guiding evidence-based care, and should be reported in a way that is reproducible, transparent and where appropriate, provide sufficient detail for inclusion in future meta-analyses. Reporting guidelines for various study designs have been widely used for clinical (and preclinical) studies, consisting of checklists with a minimum set of points for inclusion. With the

Use of informatics to characterise the exposome of COVID-19
[ad_1] The importance of exposome in precision medicine Exposome refers to the set of external exposures that affect an individual’s health from conception to death.1 This term includes all non-genetic risk factors which, interacting with the genetic endowment (genome), produce a state of health or disease (phenome). Considering these non-genetic data in precision medicine contributes to improving clinical decision making

A step-by-step guide to peer review: a template for patients and novice reviewers
[ad_1] While relatively novel, patient peer review has the potential to change the healthcare publishing paradigm. It can do this by helping researchers enlarge the pool of people who are welcome to read, understand and participate in healthcare research. Academic journals who are early adopters of patient peer review have already committed to placing a priority on using person-centred language
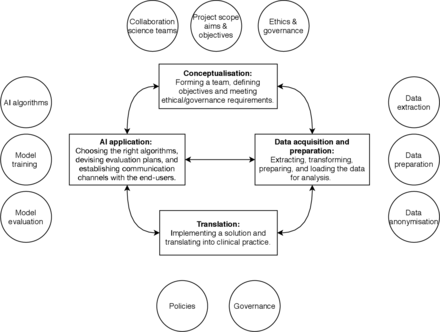
Artificial intelligence projects in healthcare: 10 practical tips for success in a clinical environment
[ad_1] Part 1. Conceptualisation 1. Build a collaborative science team No individual has all the skills and resources needed to make an AI healthcare project succeed so a collaborative science team (CST) is essential. The team’s composition may vary but includes HCPs, data scientists and possibly statisticians, project managers and software engineers. This is the most important tip; the shared
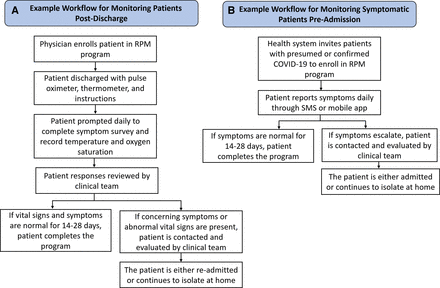
Strengthening healthcare delivery with remote patient monitoring in the time of COVID-19
[ad_1] The COVID-19 pandemic has caused unprecedented morbidity and mortality, overwhelming healthcare systems around the world. To prevent the spread of the virus, hospitals have had to severely reduce in-person visits by cancelling elective procedures and delaying routine patient visits. Recent surveys have shown a 45%–70% drop in patient visits across the USA, UK and other European nations.1 2 Simultaneously, the

The Council of Europe appoints future EDQM Director
[ad_1] The Council of Europe has appointed Petra Dörr, PhD, as future Director of the European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & HealthCare (EDQM). She will take over the function from the current Director, Susanne Keitel, in October 2021. Petra Dörr comes to the EDQM with more than 25 years of international experience in the public and private sector
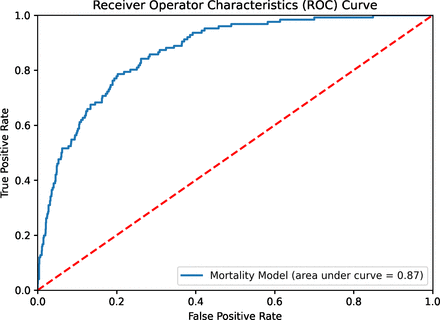
Designing COVID-19 mortality predictions to advance clinical outcomes: Evidence from the Department of Veterans Affairs
[ad_1] Results There has been a proliferation of studies evaluating risk factors behind COVID-19 infections and mortality.7 Many of these studies have assessed their performance based only on the AUROC. However, looking solely at the AUROC can lead to misleading inferences and weak predictive models since infection, as well as mortality, is so rare, meaning that over predicts negative rates
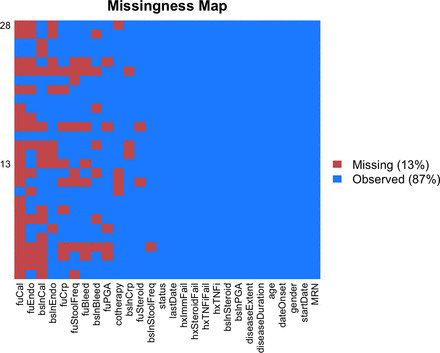
Utility of routinely collected electronic health records data to support effectiveness evaluations in inflammatory bowel disease: a pilot study of tofacitinib
[ad_1] Competing interests: Atul Butte is a co-founder and consultant to Personalis and NuMedii; consultant to Samsung, Mango Tree Corporation, and in the recent past, 10x Genomics, Helix, Pathway Genomics, and Verinata (Illumina); has served on paid advisory panels or boards for Geisinger Health, Regenstrief Institute, Gerson Lehman Group, AlphaSights, Covance, Novartis, Genentech, Merck, and Roche; is a shareholder in
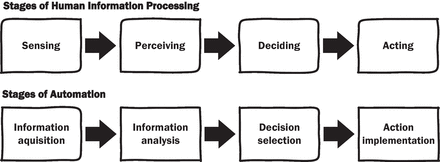
How machine learning is embedded to support clinician decision making: an analysis of FDA-approved medical devices
[ad_1] Main findings and implications The way that algorithms are embedded in medical devices shapes how clinicians interact with them, with different profiles of risk and benefit. We demonstrate how the stages of automation framework,19 can be applied to determine the stage of clinician decision making assisted by ML devices. Together with our level of autonomy framework, these methods can

COVID-19: are the elderly prepared for virtual healthcare?
[ad_1] We follow with interest the unprecedented shift towards virtual healthcare during the COVID-19 pandemic. We echo concerns reported by colleagues of the fine balance between a need for global initiatives in cutting traditional red tape to enable rapid deployment of virtual health infrastructures versus the potential risks to quality of patient care that might occur when the patient is

Survey protocol for exploring video and phone use in Aotearoa New Zealand general practice: considerations for future telehealth
[ad_1] Methods Our study is a prospective observational study. In the absence of a standardised checklist for our study, we have adopted the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology statement16 to guide the study design. The statement covers the reporting of cohort, cross-sectional and case–control studies. Since most NZ primary healthcare services and associated funding models operate within
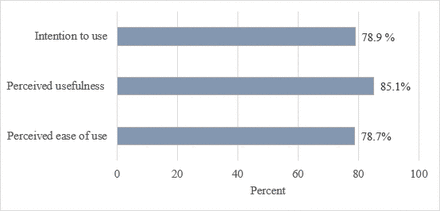
Mothers intention and preference to use mobile phone text message reminders for child vaccination in Northwest Ethiopia
[ad_1] Discussion The findings of this study showed that mothers have a high intention to use mobile phone text message reminders for their child’s vaccination. Mother’s age, educational status, duration of mobile phone use, perceived ease of use and perceived usefulness were significantly associated with intention of mothers to use mobile phone-based text message reminders for vaccination. Mothers preferred to

Clinician checklist for assessing suitability of machine learning applications in healthcare
[ad_1] Just as with a diagnostic test or a prediction rule, clinicians should be told the accuracy and reproducibility of algorithm outputs. A process of internal (or in-sample) validation should have tested and refined the algorithm on datasets resampled from the original training datasets,29 either by bootstrapping (multiple sampling in random order) or cross-validation (datasets segmented into different testing sets
EDQM reports presence of allergenic fragrances in cosmetics sold as “perfume-free”
[ad_1] A study by the European Network of Official Cosmetics Control Laboratories (OCCLs) indicates that some cosmetic products sold throughout Europe still contain excessive levels of allergy-inducing fragrances. Results showed that 7.7% of samples were non-compliant with legislative requirements due to a missing or false declaration of allergenic fragrance compounds and that 3.1% of products marketed as “perfume-free” contained fragrance
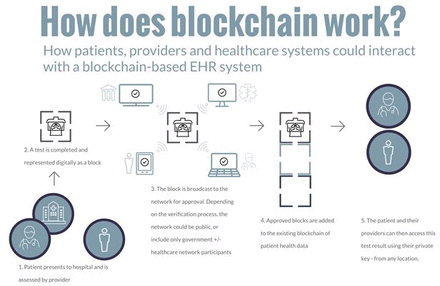
Future of blockchain in healthcare: potential to improve the accessibility, security and interoperability of electronic health records
[ad_1] Technical and safety From a technical perspective, the primary challenges are data throughput speed, file size restrictions and data security (figure 3). Select limitations of blockchain: the 3 S’s. The speed at which transactions occur on blockchain networks—known as throughput—is finite due to technical limitations. For example, the Bitcoin network processes roughly 7 transactions/s, while non-blockchain-based companies such as
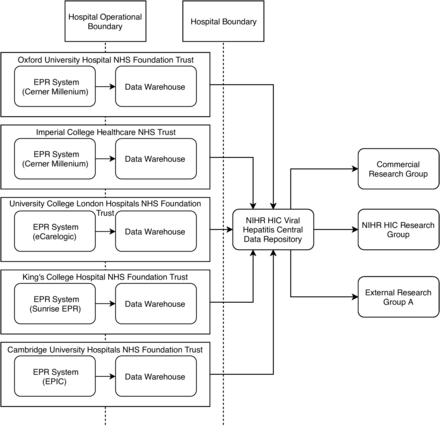
National Institute for Health Research Health Informatics Collaborative: development of a pipeline to collate electronic clinical data for viral hepatitis research
[ad_1] Results The NIHR HIC Viral Hepatitis Research Database has been developed and populated with data. Figure 3 provides an overview of the data model of the database and the relationships among different entities. The data collected falls into several categories: (a) basic information (eg, demographics, hospital visits, death, discharge and study sites), (b) laboratory data, (c) treatments, (d) diagnoses,
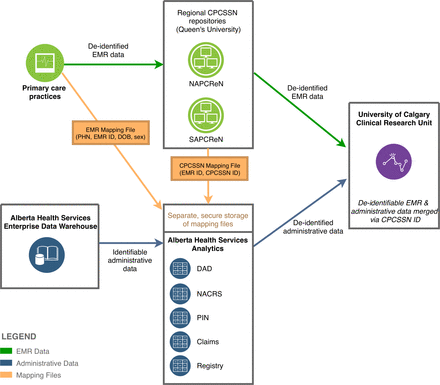
Primary care EMR and administrative data linkage in Alberta, Canada: describing the suitability for hypertension surveillance
[ad_1] Abstract Objective To describe the process for linking electronic medical record (EMR) and administrative data in Alberta and examine the advantages and limitations of utilising linked data for hypertension surveillance. Methods De-identified EMR data from 323 primary care providers contributing to the Canadian Primary Care Sentinel Surveillance Network (CPCSSN) in Alberta were used. Mapping files from each contributing provider

How telemedicine integrated into China’s anti-COVID-19 strategies: case from a National Referral Center
[ad_1] Discussion Through this analysis, it is apparent that telemedicine technologies are a legitimate mechanism for screening, triaging and treating patients with COVID-19. As echoed by other reports,4 the online platform has reduced the number of in-person visits to WCH, thereby minimising face-to-face contact among patients and clinicians and decreasing the transmission of the virus. Furthermore, limiting in-person visits reduced
