
Ahead of 2023, here are five stories that prove it’s never too late to learn something new
[ad_1] Latha Srinivasan: Dream Run At this year’s National Masters Athletics Championships, Latha Srinivasan, 62, won three silver medals — in 5K, 1500m, and 800m. She finished her first marathon last year. At an age when most people retire from sports and athletics, she has just begun. Until four years ago, her exposure to sports was limited to the occasional

National recognition to Telangana woman on the International Day of Persons with Disabilities
[ad_1] Padmavathi Pottabathini | Photo Credit: Special arrangement A journey that started as a search to find her feet steered her towards becoming a support to people with special needs. Set to receive the national award for the Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities for the year 2022 under the category Sarvshreshth Divyangan on December 3 from the President of India,
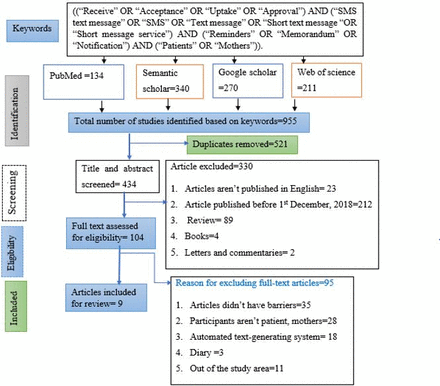
Understanding barriers of receiving short message service appointment reminders across African regions: a systematic review
[ad_1] Discussion In this systematic review, original studies focused on SMS-based medical and health service appointment reminders for any Mhealth intervention among patients, mothers or other parental figures of children across African regions were included for review. Accordingly, 9 out of the 955 searched studies were included and reviewed. A total of 11 barriers have been identified that could potentially
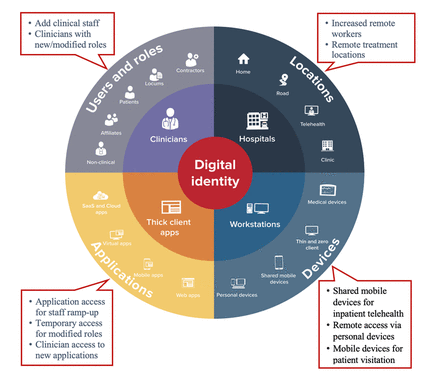
COVID-19 surge readiness: use cases demonstrating how hospitals leveraged digital identity access management for infection control and pandemic response
[ad_1] Results Table 1 summarises the hospital facility value and functional focus of each of the eight use cases reported. Table 1 View inline•Open as popup Use cases of IAM technology deployed in hospital COVID-19 response by value and functional focus SSO enabled clinicians to attest being symptom free at shift start During an outbreak of a highly transmissible pathogen

13 Thematic review of medication-related incidents at a major teaching hospital and the potential mitigation of these incidents with electronic prescribing and medicines administration
[ad_1] Abstract Objective To describe the frequency of the different types of harmful medication related incidents reported from one NHS Trust. To then assess whether the likelihood of these incidents occurring would have been reduced by a specific ePMA system, Nervecentre. Methods Two researchers retrospectively reviewed 387 medication related incidents reported to DATIX, a national reporting system, between September 2020

2 Evaluation of MaST (management and supervision tool) to support NHS community mental health teams in identifying risk of crisis and complexity across caseloads
[ad_1] Abstract Objective The Management and Supervision Tool (MaST) helps NHS mental health care professionals identify patients who are most likely to need psychiatric hospital admission or home treatment, due to severe mental illness, through a Risk of Crisis (RoC) algorithm driven by electronic health record (EHR) data analytics. MaST improves the efficiency of caseload management of Mental Health Professionals.

5 The limitations of using commercial wearable activity trackers, such as FitBits, for the clinical monitoring of patient activity levels
[ad_1] Abstract Objective There is increasing interest in remote monitoring of patients within the comfort and safety of their homes or care homes and became more pertinent during the COVID-19 pandemic to reduce hospital footfall and staff risk. While specifically designed medical devices exist, commercial wearable activity trackers (WAT), such as FitBits, are cheap, easy to use, and patients may

8 Evaluation of a telemedicine model to deliver cataract care using imaging technology instead of traditional F2F pathways
[ad_1] Abstract Objective To set up and establish a sustainable telemedicine model to deliver cataract care pathway, where the traditional face-to-face cataract assessment clinic is replaced with a telemedicine consult with imaging technology to develop a safe, efficient telemedicine care delivery model in contrast to the current established traditional face-to-face pathways. To study the efficacy, efficiency, safety, patient experience of

18 Implementing SNOMED CT in the oxford royal college of general practitioners clinical informatics digital hub (ORCHID) some problems encountered and lessons learned
[ad_1] SNOMED CT database successfully set up: Combination of experimentation, outdated advice found in grey literature, informal help from terminology expert colleague Legacy codelists: Found 350 in multiple formats, little or no provenance or definition, idiosyncratic naming. All translated in batch via cross mapping tables. Resulting outputs used as substrate for full curation. Only 154 of these taken forward. Full

12 Usability and acceptability of wearable technology in the early detection of dementia
[ad_1] Abstract Objective Digital technology is transforming health and social care. Digital technologies, which includes smartphones and wearables, can be used to predict, diagnose, monitor, and/or develop treatments for different diseases. These technologies also have the potential to detect markers of neurodegenerative diseases at a much early stage than is currently possible. The Early Detection of Neurodegeneration (EDoN) initiative aims

6 A national survey of the current provisions, perceptions and challenges regarding digital health education in the UK medical undergraduate curriculum
[ad_1] Abstract Objective Digital health (DH) is the integration of technologies to tackle challenges in healthcare. Its applications include mobile health, remote & wireless healthcare, artificial intelligence, and robotics. Digital technologies are increasingly being used to deliver routine care, whilst simultaneously patients are increasing their uptake of DH solutions (e.g. wearables). With the adoption of DH increasing across the NHS,

11 Woubot and TRUST4Health; predictive personalised AI tools for front line clinicians
[ad_1] Abstract Objective Integrating technological innovation in clinical big data from Nine Health Global (NHG) and data science Woubot is a prototype precognitive system for community & wound clinics. Focusing on leg ulcers, Woubot will produce recommendations from several thousand possible treatment combinations. Working with suppliers to the National Wound Care Strategy Programme, the project will create a suite of

7 Healthcare staff perceptions on using artificial intelligence predictive tools: a qualitative study
[ad_1] Abstract Objective Artificial intelligence (AI) predictive tools can help inform the clinical decision-making process by, for example, detecting early signs of patient deterioration or predicting the likelihood of a patient developing a particular disease or complications postsurgery. However, it is unclear how acceptable or useful clinicians find these tools in practice. This project aims to explore healthcare staff’ perceptions

17 Electronic recording of patient observations with safety functionality in the electronic health record (EHR) for the children’s hospital at in Leeds
[ad_1] Abstract Objective Electronic observations incorporating ePAWS (Paediatric Advanced Warning Score) was developed as a bespoke functionality within the EHR for implementation across the Children’s Hospital. ePAWS supports the identification of patients at risk of deterioration using a graded response strategy. To promote effective working, the functionality enables observations to be recorded via mobile device or ward computers and has

1 Digital transformation of the acute medical take – improving standards of care
[ad_1] Abstract Objective With over 50 acute medical referrals per day at Royal Bolton Hospital, an efficient and safe acute medical take process is crucial to maintain high standards of clinical care. The existing process involved multiple non-communicating patient lists to track referrals. It also relied on manual data entry – resulting in patients being missed for clerking or not

16 A friendly accessible description of the ‘L-test’ – measuring (dis)information in incomplete incident reporting
[ad_1] Abstract Objective Incomplete incident reporting is concerning. England’s Mental Health Units Use of Force Act 2018 (Seni’s Law), responding to deaths and incomplete reporting, will mandate central restraint reporting per-person including ethnicity. ‘L’ is a proposed test for disinformation, i.e. ‘false surprise’ regarding true reports. Information, or ‘surprise’, is measurable as H = -log(p) ‘bits’, as defined by Shannon

15 The data literacy learning and development needs of occupational therapists
[ad_1] Abstract Objective There is a lack of national occupational therapy impact data and occupational therapists report challenges collecting, using, and sharing information as part of professional practice. All occupational therapists need a firm grasp of data, but little is known about how confident occupational therapists feel working with data at different points in their career and in different roles

3 The documentation of allergy across electronic systems for patients presenting to emergency departments in Leeds
[ad_1] Abstract Objective How consistent is the recording of allergy documentation across multiple electronic systems in patients presenting to the emergency departments of a large UK tertiary trust? Over 20% of the UK population are affected by one or more allergic disorders (1) and there has been shown to be a 615% increase in the rate of hospital admissions for

9 Free text notes added to a patient’s allergy status in electronic prescribing systems digitally analysed for better usability
[ad_1] Abstract Objective Electronic prescribing systems often provide a drop-down list of medications and pre-specified reactions to record a patient’s allergy status. This list is non-exhaustive; less common reaction types require the user to add a free text note. The Careflow Medicines Management EPMA system provides decision support preventing a prescriber initiating a drug a patient has a recorded reaction

14 Digital health safety matters: early insights from a promising practice study in Australia
[ad_1] Abstract Objective It has been recognised that the Covid -19 pandemic positively accelerated digital adoption (Greenway et al., 2021; Issa, 2020). However, rapid deployments of technology do not often assess and understand patient safety risks; resulting in harm, which have ethical and legal considerations (HEE, 2019). The NHS has received caution of the potential risks of the use of

10 Development and evaluation of a machine learning model to predict positive urine cultures in the outpatient setting and minimize the use of antibiotics
[ad_1] Abstract Objective Excessive prescription of antibiotics is amongst the principal drivers of antibiotic resistance, which is considered a surging threat to global health. The most frequent resistant pathogens are usually linked with urinary tract diseases, such as urinary tract infections (UTI). Studies have shown that clinicians may prescribe antibiotics based on presenting symptoms due to the prolonged time required

4 Reduction of order alerts through filters: impact on pharmacists’ override rate and perceptions of alert fatigue
[ad_1] Abstract Objective Clinical decision supports (CDS) in electronic medication order systems identify alerts for clinicians. However, CDS may cause alert fatigue, which is the tendency for clinicians to ignore prompts presented by CDS due to excessive numbers and/or their perceived limited clinical significance. Alert fatigue may increase the risk of missing clinically relevant alerts. At North York General Hospital,
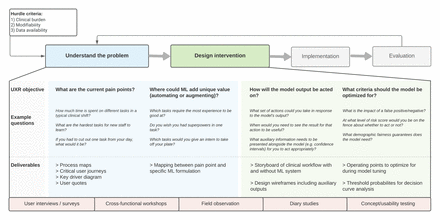
User-centred design for machine learning in health care: a case study from care management
[ad_1] Abstract Objectives Few machine learning (ML) models are successfully deployed in clinical practice. One of the common pitfalls across the field is inappropriate problem formulation: designing ML to fit the data rather than to address a real-world clinical pain point. Methods We introduce a practical toolkit for user-centred design consisting of four questions covering: (1) solvable pain points, (2)
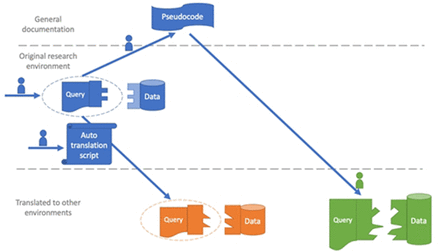
Translating electronic health record-based patient safety algorithms from research to clinical practice at multiple sites
[ad_1] Abstract Introduction Researchers are increasingly developing algorithms that impact patient care, but algorithms must also be implemented in practice to improve quality and safety. Objective We worked with clinical operations personnel at two US health systems to implement algorithms to proactively identify patients without timely follow-up of abnormal test results that warrant diagnostic evaluation for colorectal or lung cancer.
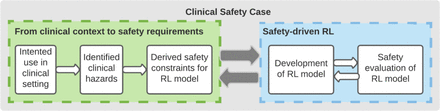
Assuring the safety of AI-based clinical decision support systems: a case study of the AI Clinician for sepsis treatment
[ad_1] Discussion Systematic safety assessment of AI-based clinical decision support systems is poorly codified, especially in applications where the definition of effective and safe decisions is challenging. In this study, we applied best practice in safety assurance to a complex AI system and proposed a safety-driven approach to identify regions of the action space potentially associated with preventable harm. We
