[ad_1]
Results
Through 2005–2014, the USA was the leading country in the health literacy field in the world with 21 128 documents. Canada and the UK ranked second and third with 3592 and 3185 scientific outputs, respectively. The results of this study indicated that Middle Eastern countries published 839 scientific papers in the field of health literacy through 2005–2014.
In terms of productivity, Iran, Turkey and Saudi Arabia have obtained the top rank among the Middle Eastern countries and have published the most papers in the field of health literacy through 2005–2014. According to PubMed database, 36.19% of these publications have been published in Iran. Turkey and Saudi Arabia by producing 19.18% and 12.18% of publications respectively, ranked second and third.
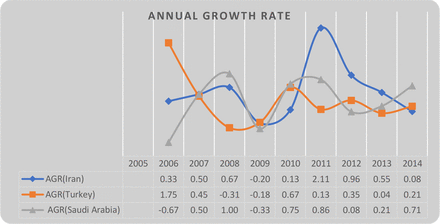
According to the results, the highest growth rate through 2005–2014 belonged to Iran in 2011; Turkey experienced the growth rate of 1.75 in 2006 and Saudi Arabia obtained the growth rate equal to 1 in 2008.
Although Turkey experienced the highest growth rate of 1.75 in publishing scientific articles in the field of health literacy, this indicator has never been repeated in the later years, in which this country has had the negative growth rate in 2008 and 2009 as well as this indicator has never exceeded 1 in Saudi Arabia.
Based on the AGR rate (figure 1), the highest rate was observed in Iran, Turkey and Saudi Arabia through 2011, 2006 and 2009, respectively. Overall, none of the mentioned countries has experienced a steady growth based on the number of publication.
Annual growth rate (AGR) of scientific publications in the field of health literacy in three top countries, during 2005–2014.
Regarding fitting of three top countries’ researches with Price’s Law, in Iran(figure 2), during the study period, the number of articles grew from 3 in 2005 to 92 in 2014. A significant correlation between the number of articles and the year was observed with a high coefficient of determination. All of the exponential, linear and log curve fitting indicated that there was a high growth rate for annual articles but it was higher in exponential model. The linear, exponential and log fitting curve for health literacy researches in Iran were found to be 0.93, 0.78 and 0.53 respectively.
Growth of scientific production on health literacy research in Iran.
In regard to productivity, over the last 10 years, there have been increase in the number of publications generated in the field of health literacy in Saudi Arabia (figure 3). The mathematical adjustment to an exponential, linear and log curve permit us to obtain a correlation coefficient r=0.76 in exponential model, indicating 24% of variance unexplained by this fitting. In contrast, the linear and log adjustment of the measured values provide correlation coefficients r=0.74 and r=0.47, respectively. With these data, we can conclude that the repertoire analysed is more in keeping with an exponential fitting than a linear one, and that the postulates of Price’s Law are fulfilled.
Growth of scientific production on health literacy research in Saudi Arabia.
In Turkey, the results also fall into line with Price’s Law of exponential growth (r=0.80 in the linear adjustment, unexplained variance of 20% vs r=0.73 in the linear adjustment, unexplained variance of 27%) (figure 4).
Growth of scientific production on health literacy research in Turkey.
The mathematical adjustment to an exponential curve as shown in figure 4 permitted us to calculate a correlation coefficient r=0.80, indicating 20% of variance unexplained by this fitting. In contrast, the linear adjustment of the measured values provides an r=0.7, with a portion of unexplained variance of 30%. With these data, we can conclude that the database analysed was more in keeping with an exponential fitting than a linear one, and that the postulates of Price’s Law were fulfilled.
The correlation of scientific production in three countries with GDP of each country indicated the positive correlation in Saudi Arabia and Turkey and negative one in Iran (figure 5).
Relationship between production of scientific publications on health literacy in three top countries and population, In addition, correlation between production of scientific output and gross domestic product (GDP) indicator.
Correlation between paper productivity and the population of each country has shown the quite similar distribution, except for Iran that has shown positive correlation.
[ad_2]
Source link